What is a signal. Types of signals
Practically from the very moment of originhuman tribes are faced with the need not only to accumulate information, but also to exchange it with each other. However, if it was not so difficult with neighbors to do it (language and writing), then with those who were at long distances, this process caused some problems.
Over time, they were solved by the inventionsignal. Types of signals were initially quite primitive (smoke, sound, etc.), but gradually humanity discovered new laws of nature, which contributed to the invention of new ways to transfer information. Let's find out what kinds of signals are, and also consider which of them are most often used in modern society.
What is called a signal
This word means information coded by one system, which is transmitted through a special channel and can be decoded by another system.

Many scientists believe that the abilitybiological organisms or even individual cells to interact with one another (signaling the presence of nutrients or danger) has become the main driving force of evolution.
Each person can act as a signalThe physical process whose parameters are adapted to the type of data being transmitted. For example, in a telephone system, the transmitter converts the words of a talking subscriber into an electrical voltage signal that is transmitted to the receiving device by wires, near which the listening person is located.
Signal and message
These two concepts are very close in meaning - they contain certain data transmitted from the sender to the recipient. However, there is a tangible difference between them.
To implement the goal, the message must necessarily be received by the addressee. That is, its life cycle consists of three stages: encoding information - transmission - decoding the message.
In the case of a signal, its acceptance is not a prerequisite for its existence. That is, the information encrypted in it can be decoded, but whether it will be done by someone is unknown.
Classification according to different signal criteria: main types
In nature there are many varietiessignals having different features. In connection with this, various criteria for these phenomena are used for their classification. Thus, three categories are distinguished:
- By the method of filing (regular / irregular).
- By the type of physical nature.
- By type of function that describes the parameters.
Signals by type of physical nature
Depending on the mode of formation, the types of signals are as follows.
- Electrical (information carrier - time-varying current or voltage in the electrical circuit).
- Magnetic.
- Electromagnetic.
- Thermal.
- Signals of ionizing radiation.
- Optical / light.
- Acoustic (sound).
Types of signals, the last two are also the simplest examples of communication technical operations, the purpose of which is to inform about the peculiarities of the situation.
Most often they are used to warn of the danger or malfunctions of the system.

Often, sound and optical varietiesare used as coordinating for the adjusted work of the automated equipment. So some kinds of control signals (commands) are stimulating for the system to start acting.
For example, in fire alarm systems withdetection of smoke traces by sensors they produce a piercing sound. That, in turn, is perceived by the system as a control signal for extinguishing the source of ignition.
Another example of how a signal (typessignals according to the type of physical nature listed above) activates the system in case of danger, is the thermoregulation of the human body. So, if, due to various factors, the body temperature rises, the cells "inform" the brain about it, and it includes the "body cooling system", better known to everyone as sweating.
By function type
In this parameter, different categories are distinguished.
- Analog (continuous).
- Quantum.
- Discrete (impulse).
- Digital signal.
All these types of signals are electrical. Due to the fact that they are not only easier to handle, but they are easily transferred for long distances.
What is an analog signal and its types
Such a name is a signal of natural origin, changing continuously in time (continuous) and capable of taking different values over a certain interval.
Due to their properties, they are perfectly suited for data transmission in telephone communications, broadcasting, and television.
In fact, all other types of signals (digital, quantum and discrete) are inherently converted analogues.
Depending on the continuous spaces and corresponding physical quantities, different kinds of analog signals are allocated.
- Straight.
- Line segment.
- Circle.
- Spaces characterized by multidimensionality.
Quantized signal
As already mentioned in the last paragraph, this is allThe same analog form, but its difference is that it was quantized. At the same time, the whole range of its values was subdivided into levels. Their number is represented in the numbers of a given digit.

Usually this process is used in practice when compressing audio or optical signals. The more quantization levels, the more accurate becomes the transformation of an analogue view into a quantum one.
The considered variety also refers to those that originated artificially.
In many classifications of signal types this signal is not allocated. However, it exists.
Discrete View
This signal also refers to artificial signals and has a finite number of levels (values). As a rule, there are two or three.

In practice, the discrete and analogways of signal transmission can be illustrated by comparing the recording of sound on a vinyl record and a CD. On the first the information is submitted in the form of a continuous sound track. But on the second - in the form of points burned by the laser with different reflecting ability.
This type of data transfer occurs by converting a continuous analog signal into a set of discrete values in the form of binary codes.
The process is called sampling. Depending on the number of symbols in code combinations (uniform / non-uniform), it is divided into two types.
Digital Signals
Today, this method of transferring information persistently replaces the analog. Like the two previous ones, it is also artificial. In practice, it is represented as a sequence of numerical values.
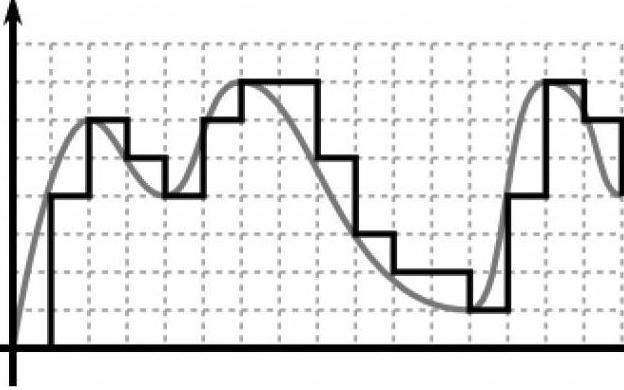
In contrast to the analogue, a muchfaster and higher quality transmits data, while cleaning them from noise interference. At the same time, this is the weakness of the digital signal (the other types of signals are in the previous three paragraphs). The fact is that the information filtered in this way loses the "noisy" particles with the data.
In practice, this means that whole pieces disappear from the transmitted image. And if we are talking about sound - words or even whole sentences.
In fact, any analog signal can bemodulated to digital. For this, it is simultaneously subjected to two processes: sampling and quantization. As a separate way of transmitting information, the digital signal is not divided into views.
His popularity contributes to the fact that inIn recent years, new generation TVs have been created specifically for digital, not analogue, transmission of images and sound. However, they can be connected to conventional TV cables using adapters.
Modulation of signals
All of the above methods of data transmission are associated with a phenomenon such as modulation (for digital signals - manipulation). Why is it needed?
As is known, electromagnetic waves (with the help ofwhich carry different types of signals) are prone to attenuation, and this significantly reduces the range of their transmission. To prevent this, low-frequency oscillations are transferred to the region of long high-frequency waves. This phenomenon is called modulation (manipulation).

In addition to increasing the transmission distance,due to it the noise immunity of signals increases. And also there is an opportunity simultaneously to organize simultaneously several independent channels of information transfer.
The process itself is as follows. The device, called a modulator, receives two signals simultaneously: low-frequency (carries certain information) and high-frequency (non-informational, but capable of transmitting for long distances). In this device they are transformed into one, which simultaneously combines the advantages of both of them.
The types of output signals depend on the modified parameter of the input carrier of the high-frequency oscillation.

If it is harmonic, such a modulation process is called analog.
If the periodic - impulse.
If the carrier signal is simply a direct current - such a variety is called noise-like.
The first two types of modulation of signals, in turn, are divided into subspecies.
Analog modulation happens this way.
- Amplitude (AM) - change in the amplitude of the carrier signal.
- Phase (FM) - the phase changes.
- Frequency - only the frequency is affected.
Types of modulation of pulsed (discrete) signals.
- Amplitude-pulse (AMI).
- Frequency-pulse (PFM).
- Pulse width (PWM).
- Phase-pulse (FIM).
Having considered what transmission methods existdata, it can be concluded that, regardless of their type, they all play an important role in human life, helping them to develop comprehensively and protect against possible dangers.
As for the analog and digital signals (withwith the help of which information is transmitted in the modern world), then, most likely, in the next twenty years in the developed countries the first will be almost completely replaced by the second.













