Pale toadstool: what are the symptoms of poisoning?
To date, a pale toadstool is consideredone of the most toxic, toxic fungi. Poisoning it leads to death in almost 99% of cases. That is why information about what this fungus looks like, what are the first symptoms of poisoning and the rules of first aid, should be known to every person.
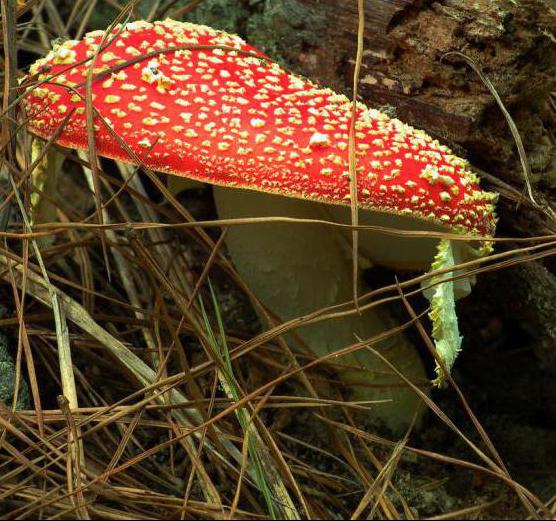
What does a pale toadstool look like?
This fungus belongs to the hats. His hat is quite large, its diameter is from five to fifteen centimeters. Pale toadstool is a plate mushroom. On the bottom surface of the bonnet there are clearly visible loose white plates. Its upper surface, as a rule, is gray, but it can also have a greenish or even olive color.
This species is quite common in Europe,North America and Asia. Usually these mushrooms grow near such trees as hazel, beech or oak. The season of pallid trash begins in the last summer month and lasts until the end of autumn.
Quite often inexperienced mushroom pickers confuse this mushroom with russules or champignons. But with unfamiliar mushrooms you need to be very careful - if in doubt, better do not touch them.
Poisoning with pale toadstool
As a rule, the first symptoms of poisoningappear 6-30 hours after the consumption of the fungus. The venom of pale toadstool consists of two kinds of toxins that are quite heavy for the body. Amanitins are very poisonous, but they act on the body relatively slowly. In the tissues of the fungus, there are also phalloidins, which are less toxic, but their action begins almost instantaneously.
Both toxins affect first of allhepatocytes of the liver. Under the influence of poison, the nucleus and other organelles of the cells are destroyed. In fact, the poisoning manifests itself in the rapid fatty degeneration of the liver, leading to very sad consequences.
The main symptoms of poisoning
Pale toadstool causes all the characteristic symptomsdisturbance of the digestive tract. A man complains of nausea, severe abdominal pain and diarrhea. Poisoning is accompanied by weakness and strong, constant thirst. It is worth noting that frequent vomiting and diarrhea in some cases leads to the development of dehydration, which only worsens the patient's condition. This poisoning period can last from one to six days.
Then begins a short period of well-being -this is the danger to man. After all, all the main symptoms disappear, and the state of health quickly improves. Some people prefer to postpone visiting a doctor. Nevertheless, after 24 hours (sometimes less) all signs of intoxication are returned in even worse form.
Now all the symptoms of toxichepatitis A. The liver is enlarged, the patient complains of the heaviness in the side, there is jaundice of the skin, a sclera of the eyes and mucous membranes. In the future, hepatic or renal failure develops.
Poisoning with mushrooms: what to do?
First of all, it should be noted that the fasterthe patient will seek medical help, the higher the chances of a favorable outcome. In the first few hours after consuming the fungus, when the food has not yet fully digested in the digestive tract, it is necessary to induce vomiting. In addition, it is recommended to give the patient activated charcoal: you need to take the medicine at a dose of 1 g per kilogram of weight. This is the effective rule of first aid. Remember that the patient should be sent to the hospital as soon as possible.
Unfortunately, the diagnosis of poisoning - not too mucha simple process, since there are no quick ways to determine the presence of toxins. That's why if you ate mushrooms (even if you are not sure that it was just a pale toadstool), be sure to mention this when talking to your doctor.
As for the treatment, it is necessary firstmaintain a balance of fluid and electrolytes in the blood. To this end, the patient is administered saline. As for the antidote among medical staff, there is no single opinion. But the statistics show that if you start treatment with antidotes in the first three days after the poisoning, then the chance of recovery is very high. In some cases, dialysis is prescribed for rapid detoxification.